Oral surgery and
implantology
In our office it is possible to compensate for the lost teeth without scraping the adjacent teeth. This is achieved by placing dental implants, which can replace individual teeth or be included in the plan for making other larger prosthetic implants. Unlike conventional surgery, oral surgery does not require a hospital stay. In fact, many of the procedures performed in our dental practice, including tooth extraction, wisdom tooth extraction, and frenulectomy, are considered oral surgery, and they involve the application of local anesthetics and certain pain control medications.
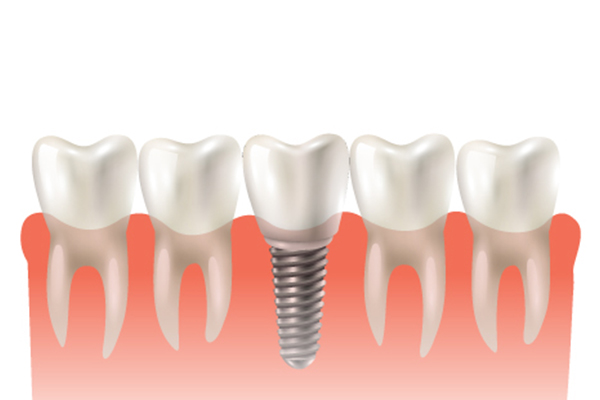
Dental
Implants
A dental implant is a type of screw that is inserted into the jaw bone and serves as a replacement for the missing tooth (its root part). Dental implants are usually made of titanium, a metal that is biocompatible and does not cause allergies.
Implant placement can be:
• Standard implantation - the dental implant is placed in the place of the missing tooth
• Immediate implantation - the implant is placed immediately (or up to 7 days) after tooth extraction, thus preventing bone resorption.
The surgical procedure for placing a dental implant takes a short time and is completely safe and painless. After placement of dental implants, the waiting period for osseointegration (bone fusion) is between 3 and 6 months. Implants are the best solution in the absence of one, more or all teeth in one or both jaws.

Extraction
of teeth
Although permanent teeth are a dentition that from the outset should persist in the mouth throughout life, most of us have the need to extract certain teeth for a number of reasons. Some of the factors that condition extraction are: trauma, caries processes that have destroyed the tooth tissues or infection, or in case of discomfort (lack of space in the mouth for all teeth). Regardless of why a tooth needs to be extracted, this intervention gives no cause for fear or concern. Immediately after the extraction of the tooth, in our office you will receive a series of proposals for aesthetic and functional compensation of the lost tooth.
Frenulectomy
Frenulectomy is the simple removal of frenulum in the mouth. The frenulum is a muscular attachment between two tissues. There are two frenulums in the mouth that can sometimes interfere with normal function and they recommend this intervention. These frenulum are called the lingual frenulum, which connects the tongue to the floor of the oral cavity, and the maxillary labial frenulum, which connects the inside of the upper lip to the palate just above the upper central incisors.
In the upper jaw it may be the cause of diastema (space) between the upper central incisors due to high attachment. In the lower jaw, a thickened frenulum causes difficulty in lifting the tongue, and in some situations causes difficulty in speaking. Frenulum removal is a routine incision of the frenulum that is performed painlessly, under local anesthesia, without leaving any scar after healing.
Apicoectomy
Apicoectomy is a surgical procedure in which an inflammatory process is to be removed from the bone along with the tip of the root of the decayed tooth that caused the process. Surgical treatment involves making small incisions in the soft tissue and opening a small window through the bone to access the root of the tooth, removing the infection around the tip of the tooth root as well as the tip (only a few millimeters). To complete the apicoectomy, the tip of the tooth is filled and sealed with a special cement to prevent recurrence of the infection. Finally, the wound is sutured and the sutures are removed after a week. The time required to complete treatment depends on the infection and the number of roots to be treated. It is recommended that a follow-up scan and clinical examination be performed after one year to control bone formation and filling in the remaining gaps.
Sinus
lift
Sinus lift is a surgical procedure in which the bottom of the maxillary sinus is raised and a bone is added to the upper jaw in the region of the molars and forearms. The sinus lift involves accessing the sinus cavity, lifting its mucous membrane, and inserting an artificial bone into the interstitium. A sinus lift is done when there is not enough bone in the upper jaw, or the sinuses are too close to the jawbone to get a bigger bone base to place implants.
The assessment of the need for a sinus lift is performed on 3D images. The procedure itself is painless and is performed under local anesthesia.
